Method:
1) Clean the copper coin with the wire wool.
2) Add five grams of zinc powder into the water ( Now you have made the solution).
3) Now turn on the bunsen burner to boil the solution.
4) Once the solutions are boiling then add the copper coin.
5) Once the copper coin turns silver lift it out the glass beaker.
6) Now put the silver coin in some water to cool down.
7) Take the coin out of the water and dab it dry with a tissue.
8) Now take the coin using the beaker tongs and put it on the flame of the bunsen burner.
9) flipping it occasionally
Equipment: Wire wool, Five grams of zinc powder, beaker, Bunsen burner, gauze mat, tripod, tissue, beaker tongs.
Result: This experiment turned out great this is what my coin turned out like:
Discussion:
An alloy is a mixture of two or more elements, one or more of which is a metal. Alloys often have properties that are different from the metals they contain. This makes them more useful than the pure metals alone. For example, alloys are often harder than the metal they contain. Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. It is used to make many things such as cars, ships, bridges, and building frames. Steel is harder, stronger and more flexible than iron and doesn't corrode (rust) as quickly as iron. Other examples of Alloys are brass, bronze, pewter, cast and wrought iron, coin metals, and solder. Alloys have special properties, They are more conductive to heat or electricity, less prone to rust or corrosion. Alloys are made by melting metals, mixing them while they are soluble to form a solution, Then leave them to cool and turn into a solid again. There are two different alloys, one is called substitution alloys and the other is called interstitial alloys. In substitution alloys, the atoms of the original metal are literally replaced with atoms that have roughly the same size from another material. Brass, for example, is an example of a substitution alloy of copper and zinc. Aluminum alloys contain next to no iron and without any iron, the alloys cant actually rust. It does however oxidize. When the alloy is exposed to water, a film of aluminum oxide forms quickly on the surface. The oxide layer is resistant to further corrosion and protects the metal.
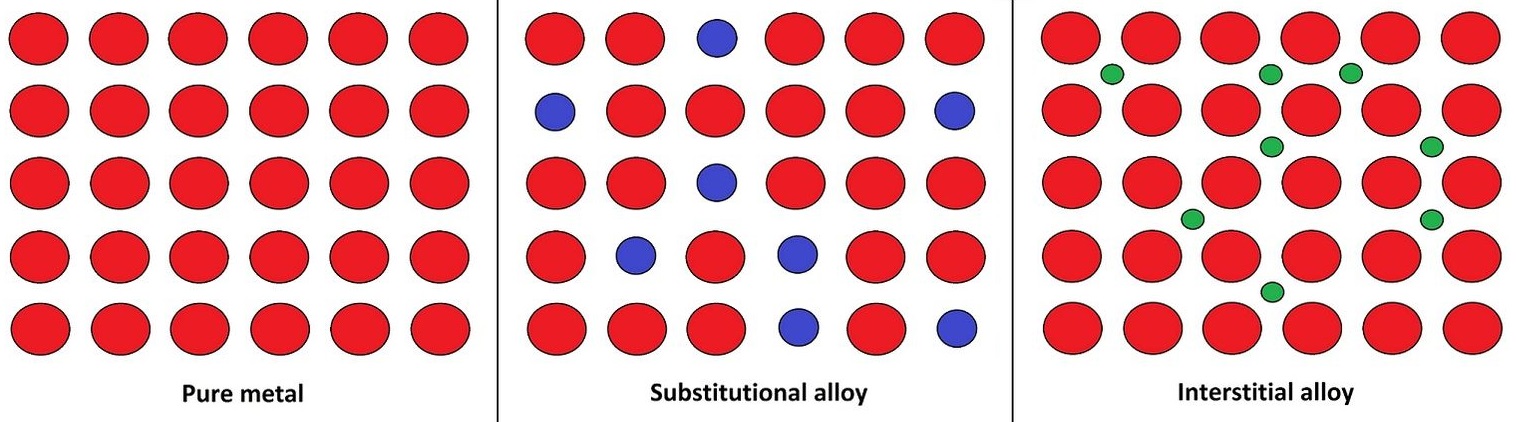
Substitution alloy and Interstitial alloy
Substitution alloys are when you replace one atom with another that is of the same size as the photo above shows whereas Interstitial alloys are where the other atom occupies the spaces in between the former metal atoms.

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.